Protective Coatings
Protective coatings are applied to surfaces to prevent corrosion, wear, and other forms of degradation. Common types include epoxy, polyurethane, acrylic, and ceramic coatings, each offering specific benefits like chemical resistance, UV protection, or fire resistance. Other categories include galvanizing, powder coating, and various specialized coatings like anti-graffiti or hygienic coatings.
1. Epoxy Coatings
Excellent adhesion and chemical resistance; used on floors and heavy machinery.

2. Polyurethane Coatings
UV resistance and flexibility; suitable for exterior and metal surfaces.

3. Zinc Coatings (Galvanization)
Zinc acts as a sacrificial layer to protect steel from corrosion.

4. Ceramic Coatings
High-temperature and chemical resistance for extreme-heat applications.

5. Acrylic Coatings
Versatile and easy to apply; suited to less demanding environments.

6. Alkyd Coatings
Usable in various climatic conditions; durable film.

7. Silicone Coatings
Weather-resistant with high-temperature stability.
8. Intumescent Coatings
Fire-protection; expand when heated to form a protective barrier.

9. Metallic Coatings
Electroplating or thermal spray to deposit protective metal layers.
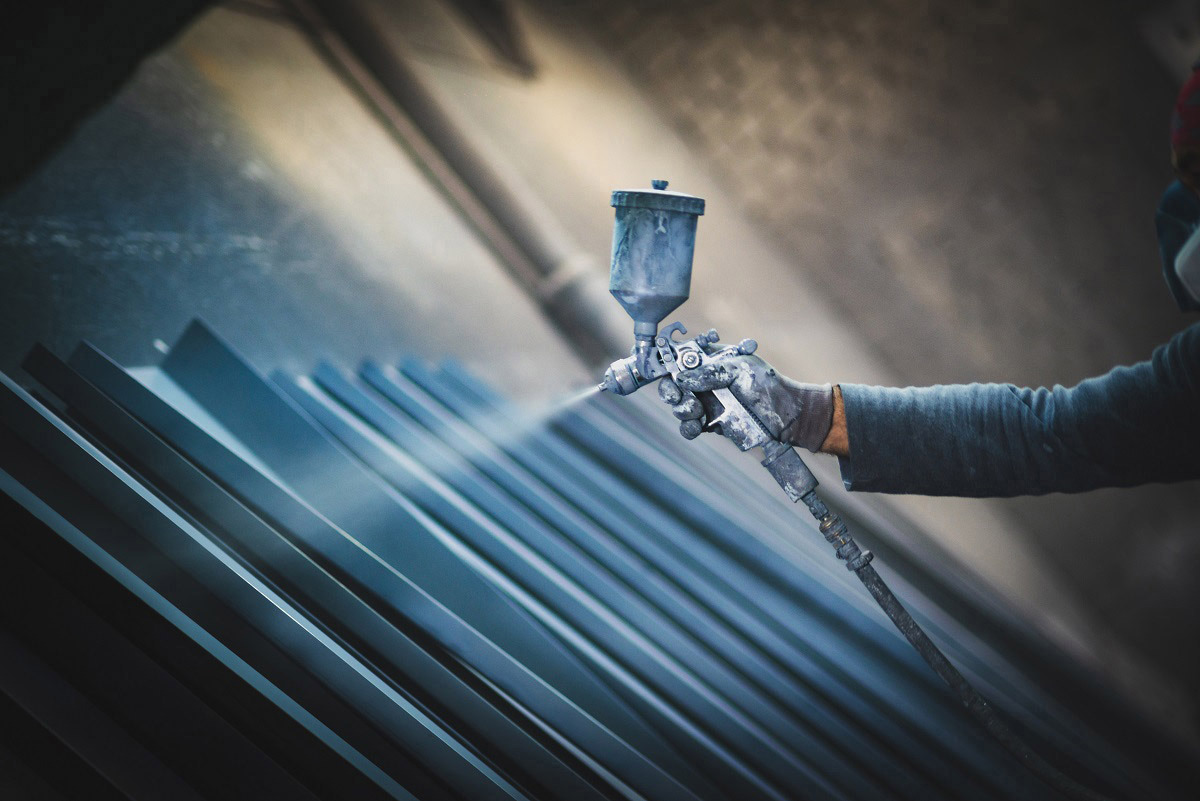

10. Organic Coatings
Polymer/resin-based films providing protective layers.
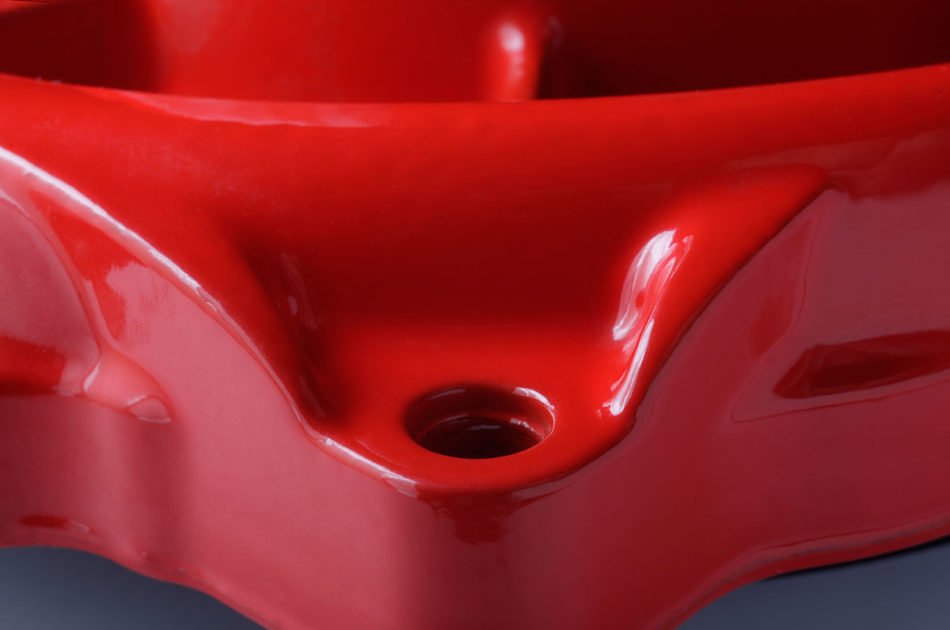

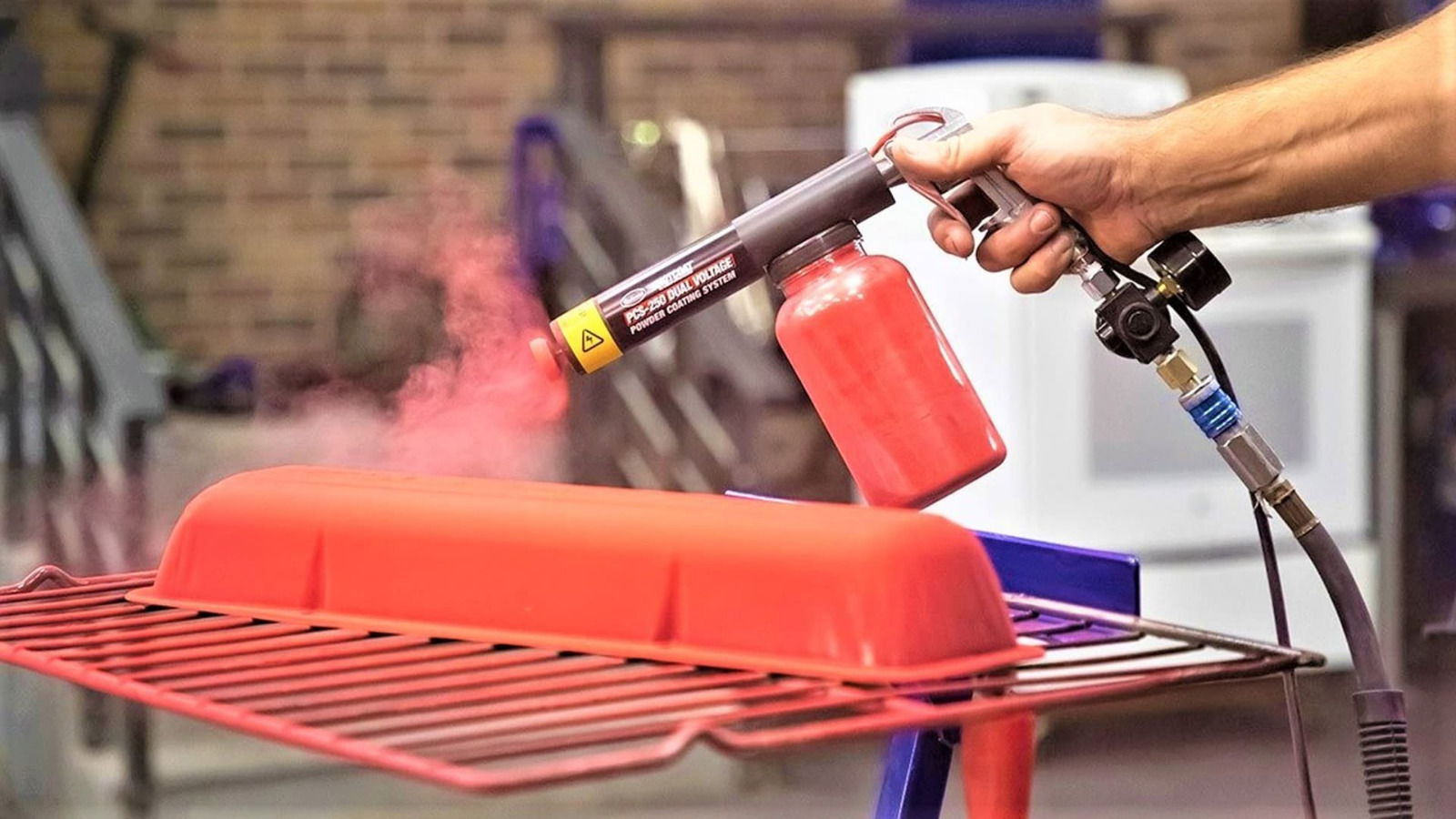
11. Powder Coatings
Dry powder applied and melted into a smooth, durable finish.

12. Cathodic Protection
Sacrificial metal or impressed current used to prevent corrosion.

13. Chromate Conversion Coating
Chemical treatment forming a corrosion-resistant film.
14. Phosphating
Phosphate layer enhances paint adhesion and corrosion resistance.

15. Anodizing
Electrochemical oxide layer, typically on aluminium.

16. Paints and Primers
Various paint systems for corrosion protection and aesthetics.

